The Java serialization algorithm revealed---reference
|
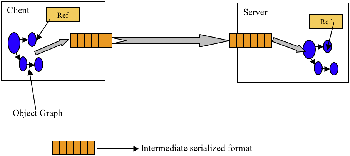
Serialization?is the process of saving an object's state to a sequence of bytes;?deserialization?is the process of rebuilding those bytes into a live object. The Java Serialization API provides a standard mechanism for developers to handle object serialization. In this tip,you will see how to serialize an object,and why serialization is sometimes necessary. You'll learn about the serialization algorithm used in Java,and see an example that illustrates the serialized format of an object. By the time you're done,you should have a solid knowledge of how the serialization algorithm works and what entities are serialized as part of the object at a low level. Why is serialization required?In today's world,a typical enterprise application will have multiple components and will be distributed across various systems and networks. In Java,everything is represented as objects; if two Java components want to communicate with each other,there needs be a mechanism to exchange data. One way to achieve this is to define your own protocol and transfer an object. This means that the receiving end must know the protocol used by the sender to re-create the object,which would make it very difficult to talk to third-party components. Hence,there needs to be a generic and efficient protocol to transfer the object between components. Serialization is defined for this purpose,and Java components use this protocol to transfer objects. Figure 1 shows a high-level view of client/server communication,where an object is transferred from the client to the server through serialization.
Figure 1. A high-level view of serialization in action?How to serialize an objectIn order to serialize an object,you need to ensure that the class of the object implements the Listing 1. Implementing Serializable=100=0
In Listing 1,the only thing you had to do differently from creating a normal class is implement the? Now that you have made the class eligible for serialization,the next step is to actually serialize the object. That is done by calling the? Listing 2. Calling writeObject()=newFileOutputStream("temp.out"==
Listing 2 stores the state of the? To re-create the object from the persistent file,you would employ the code in Listing 3. Listing 3. Recreating a serialized object=newFileInputStream("temp.out"=="version="+ts.version);}
In Listing 3,the object's restoration occurs with the Executing this code will print? The serialized format of an objectWhat does the serialized version of the object look like? Remember,the sample code in the previous section saved the serialized version of the? Listing 4. Hexadecimal form of TestSerialAC ED 6C
A0 FE B1 DD F9
6F 6E 6F 6E
If you look again at the actual? Listing 5. TestSerial's byte memberspublicbyte version =100=0;
Java's serialization algorithmBy now,you should have a pretty good knowledge of how to serialize an object. But how does the process work under the hood? In general the serialization algorithm does the following:
I've written a different example object for this section that will cover all possible cases. The new sample object to be serialized is shown in Listing 6. Listing 6. Sample serialized object parentVersion =10 containVersion =11<span style="color: #0000ff;">public<span style="color: #000000;"> classSerialTestextends parent implementsSeriali zable{
<span style="color: #0000ff;">int version =66<span style="color: #000000;">; contain con =<span style="color: #0000ff;">new<span style="color: #000000;"> contain(); publicint getVersion(){ <span style="color: #0000ff;">public <span style="color: #0000ff;">static <span style="color: #0000ff;">void<span style="color: #000000;"> main(String args[])throwsIOException{ This example is a straightforward one. It serializes an object of type? Listing 7. Serialized form of sample objectAC ED AC F6 DB D2 BD EE 637A02000149000D706172656E7456657273696F6E78700000000A0000004273720007636F6E7461696E FC BB E6 FB CB C7
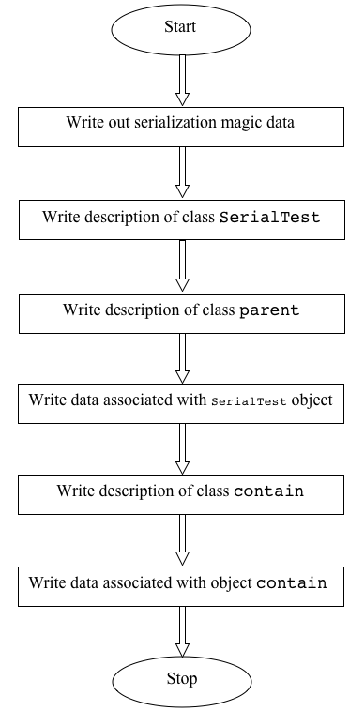
Figure 2. An outline of the serialization algorithmLet's go through the serialized format of the object in detail and see what each byte represents. Begin with the serialization protocol information:
The first step of the serialization algorithm is to write the description of the class associated with an instance. The example serializes an object of type?
Next,the algorithm writes the field
And then the algorithm writes the next field,?
The next step of the algorithm is to write the description of the?
parentclass.? parent?has one field,?int parentVersion = 100;.
So far,the serialization algorithm has written the description of the class associated with the instance and all its superclasses. Next,it will write the actual data associated with the instance. It writes the parent class members first:
Then it moves on to?
The next few bytes are interesting. The algorithm needs to write the information about the? Listing 8. The contain objectcontain con = contain();
Remember,the serialization algorithm hasn't written the class description for the?
Next,the algorithm must write the description for?
Next,the serialization algorithm checks to see if?
Finally,the algorithm writes the actual data associated with?
ConclusionIn this tip,you have seen how to serialize an object,and learned how the serialization algorithm works in detail. I hope this article gives you more detail on what happens when you actually serialize an object. About the author?has more than four years of experience in the IT industry,and has been working with Java-related technologies for more than three years. Currently,he is working as a system software engineer at the Java Technology Center,IBM Labs. He also has experience in the telecom industry. Resources
reference address: (编辑:李大同) 【声明】本站内容均来自网络,其相关言论仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本站立场。若无意侵犯到您的权利,请及时与联系站长删除相关内容! |