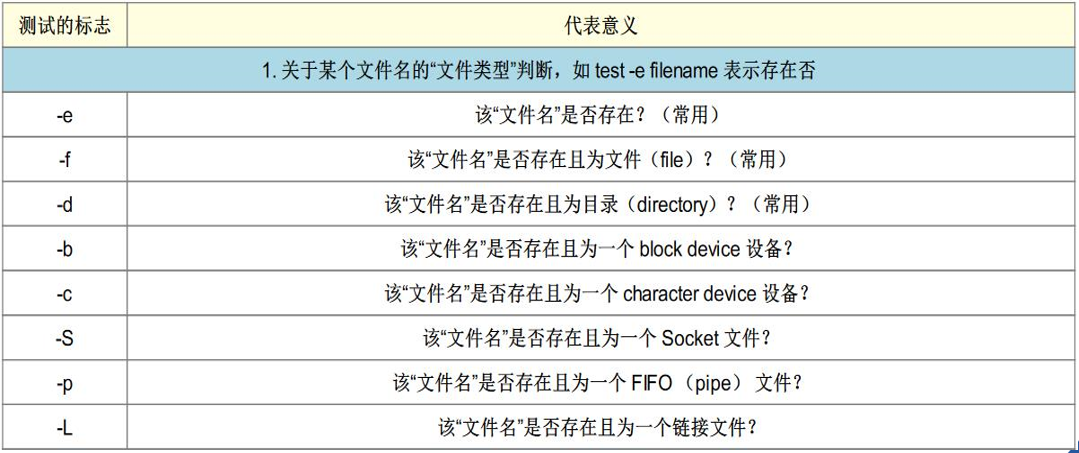
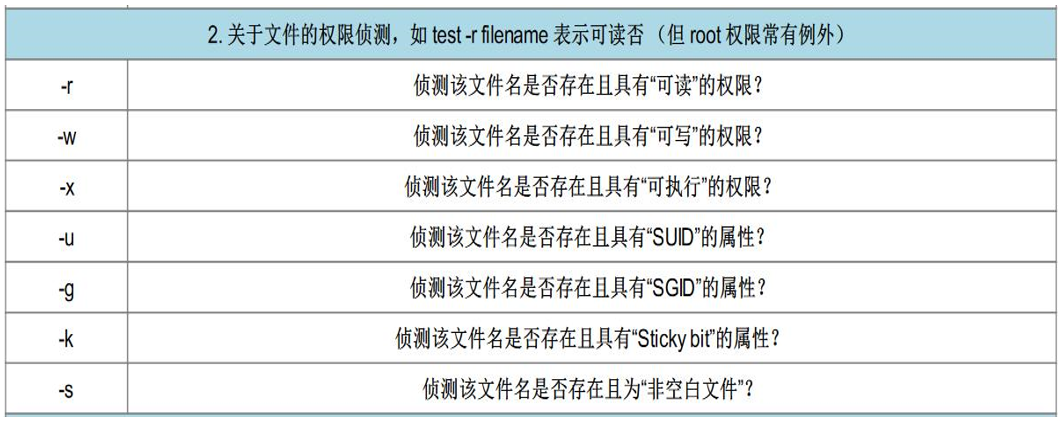
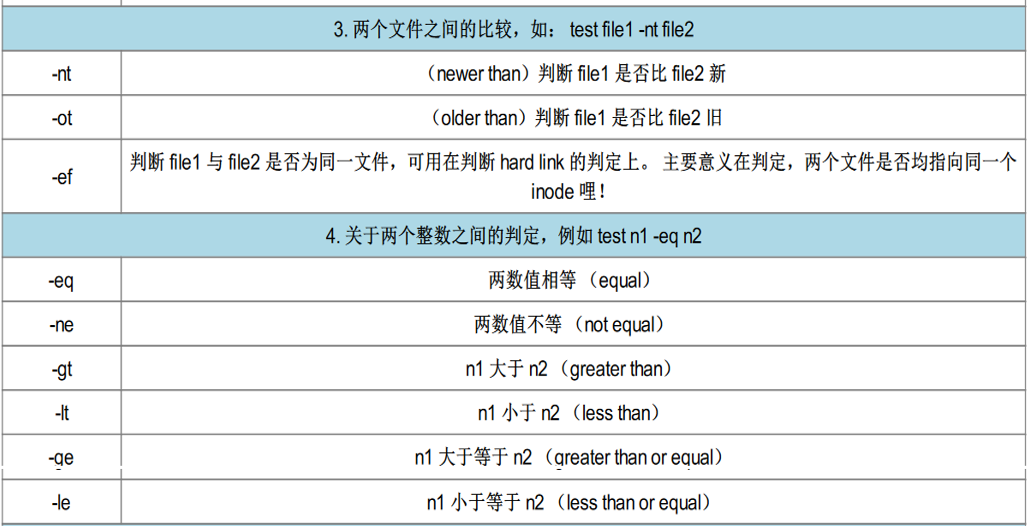
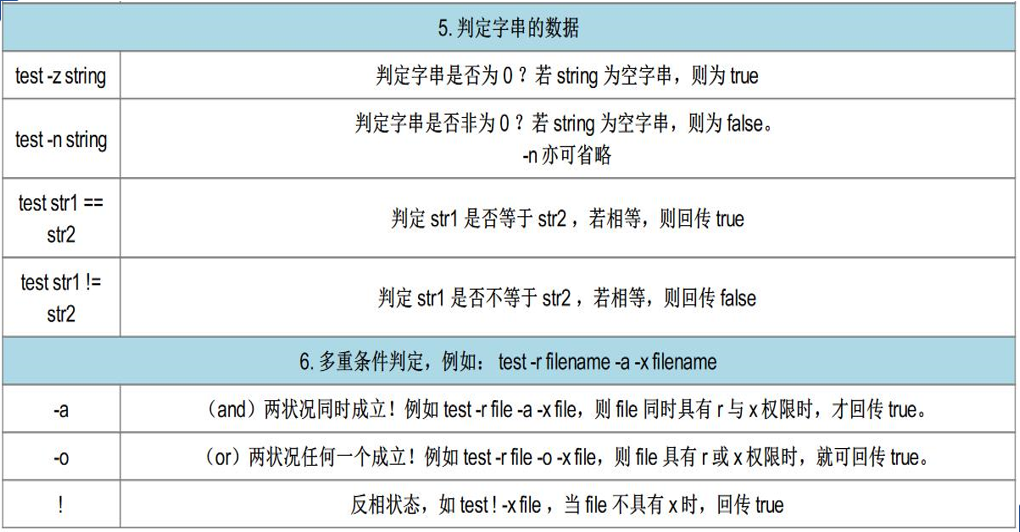
最全shell脚本语句语法使用(超详细)
|
博文大纲:
shell脚本的编写越规范越好,那么通常在每个shell脚本的开头几行会有如下几个方面相关的注释信息:
废话不多说,直接上使用语法案例: 1、对谈式脚本——read语句需求①: [[email?protected] ~]# vim 1.sh #编辑脚本,内容如下
#!/bin/bash
echo -e "yong lai xian shi wen jian full name:n"
read -p "qing shu ru fir filename:" firname
read -p "qing shu ru sec filename:" secname
echo -e "nyour full name is ${firname}${secname}."
#其中echo后面的“n”表示换行
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 1.sh #执行脚本
yong lai xian shi wen jian full name:
qing shu ru fir filename:lv #手动输入文件名开头
qing shu ru sec filename:jian #手动输入文件名结尾
your full name is lvjian. #它将自动将开头和结尾结合起来并输出
需求②: [[email?protected] ~]# vim 2.sh #编辑脚本
#!/bin/bash
echo -e "yi ci chuang jian san ge file.n"
read -p "qing shu ru filename:" filename
filename=${filename:-file}
date1=$(date --date ‘1 days ago‘ +%Y%m%d)
date2=$(date --date ‘2 days ago‘ +%Y%m%d)
date3=$(date +%Y%m%d)
file1="${filename}${date1}"
file2="${filename}${date2}"
file3="${filename}${date3}"
touch "${file1}"
touch "${file2}"
touch "${file3}"
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 2.sh #执行脚本
yi ci chuang jian san ge file.
qing shu ru filename:lv #输入自定义的文件名开头
[[email?protected] ~]# find /root -name "lv*" #查看是否创建成功
/root/lv20190825
/root/lv20190827
/root/lv20190826
需求②: [[email?protected] ~]# vim 3.sh #编辑脚本
#!/bin/bash
echo -e "nzhe shi yi ge suan cheng fa de jiao ben:n"
read -p "qing shu ru yi ge shu zi:" A
read -p "qing shu ru di er ge shu zi:" B
sum=`echo "scale=4; ${A} * ${B}" | bc`
echo -e "n${A}x${B} ==> ${sum}."
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 3.sh #执行脚本
zhe shi yi ge suan cheng fa de jiao ben:
qing shu ru yi ge shu zi:3 #输入第一个数
qing shu ru di er ge shu zi:4 #输入第二个数
3x4 ==> 12. #输出的结果
2、shell脚本中的测试的字符
上面所有的测试都是通过test进行的,可以使用“[ ]”来代替,将要测试的类型及指定的名字写在“[ ]” 即可,但是中括号里面两边必须有空格。(推荐使用中括号“[ ]”) 3、判断脚本举例需求①:
[[email?protected] ~]# vim 4.sh #编辑脚本
#!/bin/bash
echo "yong lai ce shi wen jian huo dirctory."
read -p "qing shu ru yi ge wen jian ming:" filename
test -z ${filename} && echo -e "nqing shu ru yi ge filename." && exit 0
test ! -e ${filename} && echo "filename does not exitst." && exit 0
test -f ${filename} && filetype="file"
test -d ${filename} && filetype="directory"
test -r ${filename} && prem="read"
test -w ${filename} && prem="${prem}+write"
test -x ${filename} && prem="${prem}+exe"
echo -e "nthis is a ${filetype},it‘s perm.. is ${prem}."
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 4.sh #执行脚本
yong lai ce shi wen jian huo dirctory.
qing shu ru yi ge wen jian ming:/root #输入一个目录名
this is a directory,it‘s perm.. is read+write+exe. #脚本执行后输出的结果
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 4.sh #再执行脚本
yong lai ce shi wen jian huo dirctory.
qing shu ru yi ge wen jian ming:/etc/passwd #输入一个文件
this is a file,it‘s perm.. is read+write. #脚本执行后输出的结果
需求②: 1、当执行一个程序的时候,这个程序会让用户输入Y或N。 [[email?protected] ~]# vim 5.sh #编辑脚本
#!/bin/bash
while [ "${yn}" != "Y" -o "${yn}" != "y" -o "${yn}" != "N" -o "${yn}" != "n" ]
do
read -p "qing shu ru ‘Y‘ or ‘N‘:" yn
[ "${yn}" == "Y" -o "${yn}" == "y" -o "${yn}" == "" ] && echo -e "nOK,continue." && exit 0
[ "${yn}" == "N" -o "${yn}" == "n" ] && echo -e "nON,interrupt." && exit 0
done
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 5.sh #下面是多次执行脚本,测试是否达到需求
qing shu ru ‘Y‘ or ‘N‘:
OK,continue.
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 5.sh
qing shu ru ‘Y‘ or ‘N‘:y
OK,continue.
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 5.sh
qing shu ru ‘Y‘ or ‘N‘:n
ON,interrupt.
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 5.sh
qing shu ru ‘Y‘ or ‘N‘:u
qing shu ru ‘Y‘ or ‘N‘:i
qing shu ru ‘Y‘ or ‘N‘:N
ON,interrupt.
需求③: [[email?protected] ~]# vim 6.sh #编辑脚本如下
#!/bin/bash
echo -e "ncheng xu de wen jian ming shi ${0}"
echo -e "nyi gong you $# ge can shu."
[ $# -lt 2 ] && echo "can shu tai shao le ." && exit 0
echo "your whole parameter is ==> ‘$*‘."
echo "the 1st parameter ${1}."
echo "the 2nd parameter ${2}."
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 6.sh a b c #执行脚本
cheng xu de wen jian ming shi 6.sh
yi gong you 3 ge can shu.
your whole parameter is ==> ‘a b c‘.
the 1st parameter a.
the 2nd parameter b.
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 6.sh a #再次执行脚本
cheng xu de wen jian ming shi 6.sh
yi gong you 1 ge can shu.
can shu tai shao le .
#为了不为难自己,上面我用了拼音,多多体谅[ 捂脸 ]。
需求④: [[email?protected] ~]# vim 11.sh
#!/bin/bash
file="/dev/shm/a.txt"
netstat -anpt > ${file}
awk -F : ‘{print $4}‘ ${file} | awk ‘{print $1}‘ | grep "80" &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo -e "www service is upn"
fi
awk ‘{print $4}‘ ${file} | egrep "20|21" &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo -e "ftp service is upn"
fi
awk ‘{print $4}‘ ${file} | grep "25" &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo -e "mail service is upn"
fi
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 11.sh #执行脚本测试
mail service is up
[[email?protected] ~]# systemctl start httpd #启动www服务再测试
[[email?protected] ~]# sh 11.sh
www service is up
mail service is up
需求⑤: [[email?protected] ~]# vim 7.sh #编辑脚本如下 #!/bin/bash echo "total parameter number is ==> $#" echo "your whole parameter is ==> $* " shift echo "total parameter number is ==> $#" echo "your whole parameter is ==> $* " shift 3 echo "total parameter number is ==> $#" echo "your whole parameter is ==> $* " #“上面默认的shift”参数是偏移1个位置,也可以指定偏移的参数,如“shift 3”则表示向后偏移三个 [[email?protected] ~]# sh 7.sh a b c #执行脚本,并且追加三个参数 total parameter number is ==> 3 your whole parameter is ==> a b c total parameter number is ==> 2 your whole parameter is ==> b c total parameter number is ==> 2 your whole parameter is ==> b c #从输出结果可以发现,偏移是累加的,第一次偏移了默认1位, #第二次偏移了3位,那么实际已经偏移了原始参数的4位(因为累加) #但是参数只有三个,所以它会循环偏移,所以结果还是b和c。 关于上面脚本中的“$#”、“$*”的解释可以参考如下解释:
4、条件判断——if语句需求①: 1、当执行一个程序的时候,这个程序会让用户输入Y或N。 [[email?protected] ~]# vim 11.sh #编写脚本 #!/bin/bash read -p "Please input (Y/N): " yn (编辑:李大同) 【声明】本站内容均来自网络,其相关言论仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本站立场。若无意侵犯到您的权利,请及时与联系站长删除相关内容! |