JavaScript概述
ECMAScript和JavaScript的关系
1996年11月,JavaScript的创造者–Netscape公司,决定将JavaScript提交给国际标准化组织ECMA,希望这门语言能够成为国际标准。次年,ECMA发布262号标准文件(ECMA-262)的第一版,规定了浏览器脚本语言的标准,并将这种语言称为ECMAScript,这个版本就是1.0版。
?
该标准一开始就是针对JavaScript语言制定的,但是没有称其为JavaScript,有两个方面的原因。一是商标,JavaScript本身已被Netscape注册为商标。而是想体现这门语言的制定者是ECMA,而不是Netscape,这样有利于保证这门语言的开发性和中立性。
?
因此ECMAScript和JavaScript的关系是,前者是后者的规格,后者是前者的一种实现。
ESMAScript的历史
| 年份 |
名称 |
描述 |
| 1997 |
ECMAScript 1 |
第一个版本 |
| 1998 |
ECMAScript 2 |
版本变更 |
| 1999 |
ECMAScript 3 |
添加正则表达式,添加try/catch |
| ? |
ECMAScript 4 |
没有发布 |
| 2009 |
ECMAScript 5 |
添加"strict mode"严格模式 添加JSON支持 |
| 2011 |
ECMAScript 5.1 |
版本变更 |
| 2015 |
ECMAScript 6 |
添加类和模块 |
| 2016 |
ECMAScript 7 |
增加指数运算符(**), 增加Array.prototype.includes |
注: ES6就是指ECMcript 6
尽管ECMAScript是一个重要的标准,但它并不是 JavaScript 唯一的部分,当然,也不是唯一被标准化的部分。实际上,一个完整的 JavaScript 实现是由以下 3 个不同部分组成的:
JavaScript引入方式
在HTML中,不限制脚本数量 一般javascript都会放在header标签里面,以不干扰页面内容. javascript语句向浏览器发出什么指令,告诉浏览器该做什么
Script标签内写代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<H1>幽梦</H1>
?
<script>
? ?alert("YouMen")
</script>
</body>
</html>
引入额外的JS文件
<script src="myscript.js"></script>
?
JavaScript语言规范
分号
语句之间的分割是分号(;) 注意: 分号是可选项,有时候看到不以分号隔开的.
标识符
JavaScript标识符必须以字母,下划线或美元符号开始 JavaScript关键字 JavaScript同样对大小写很敏感.
注释
<body>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?
空格并不影响代码执行
结束符
JavaScript的语句是以分号(;)为结束符。
变量声明
变量是存储信息的容器
数据类型
数值(Number)类型
JavaScript不区分整型和浮点型,就只有一种数字类型。
还有一种NaN,表示不是一个数字(Not a Number)。
常用方法:
字符串(String)类型
var a = "Hello"
var b = "world;
var c = a + b;
console.log(c); ?// 得到Helloworld
a.substring(1,3)
"el"
?
?
常用方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
| .length #不加括号的是属性 |
返回长度 |
| .trim() #得到一个新值 |
移除空白 |
| .trimLeft() |
移除左边的空白 |
| .trimRight() |
移除右边的空白 |
| .charAt(n) #n类似索引,从0开始,超过最大值返回''空字符串 |
返回第n个字符 |
| .concat(value,...) #s1='hello';s.concat('xx');得到helloxx |
拼接 |
| .indexOf(substring,start) #这个start是从索引几开始找,没有返回-1 |
子序列位置 |
| .substring(from,to) #不支持负数,所以一般都不用它,了解一下就行了 |
根据索引获取子序列 |
| .slice(start,end) #var s1='helloworld';s1.slice(0,-5)看结果,就用它 |
切片 |
| .toLowerCase() #全部变小写 |
小写 |
| .toUpperCase() #全部变大写 |
大写 |
| .split(delimiter,limit)#分隔,s1.splite(' '),后面还可以加参数s1.split(' ',2),返回切割后的元素个数 |
分割 |
?
数据类型转换
var a = '123abc'
undefined
var b = parseInt(a);
undefined
typeof(b)
"number"
?
?
?
Example1 定时器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?
Example2 跑马灯
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<div id="i1">北京欢迎你</div>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?function func() {
? ? ? ? ? ?var tag = document.getElementById('i1');
? ? ? ? ? ?
字符串切片
布尔类型(Boolean)
布尔值区别于Python,true和false都是小写.
var a = true;
var b = false;
?
# "(空字符串),null,undefined,NaN都是false.
?
# null 和undefined
# null 表示值是空,一般在需要指定或清空一个变量才会使用,如name=null;
# undefined表示当声明一个变量但未初始化时,该变量的默认值是undefined,还有就是函数无明确的返回值时,返回的也是undefined.
?
# null表示变量的值是空(null可以手动清空一个变量的值,使得该变量变为object类型,值为null),
# undefined则表示只声明了变量,但没有赋值.
?
对象(Object)
JavaScript中的所有事物都是对象; 字符串、数值、数组、函数..此外,JavaScript允许自定义对象. JavaScript提供多个内建对象,比如String、Date、Array等等. 对象只是带有属性和方法的特殊数据类型.
?
数组
数组对象的作用是:使用单独的变量名来存储一系列的值。类似于Python中的列表。
常用方法:
| 方法 |
说明 |
| .length |
数组的大小 |
| .push(ele) |
尾部追加元素 |
| .pop() |
获取尾部的元素 |
| .unshift(ele) |
头部插入元素 |
| .shift() |
头部移除元素 |
| .slice(start,end) |
切片 |
| .reverse() |
反转 |
| .join(seq) |
将数组元素连接成字符串 |
| .concat(val,...) |
连接数组 |
| .sort() |
排序 |
| .forEach() |
将数组的每个元素传递给回调函数 |
| .splice() |
删除元素,并向数组添加新元素。 |
| .map() |
返回一个数组元素调用函数处理后的值的新数组 |
splice()
语法: splice(index,howmany,item1,.....,itemX)
参数:
参数:
| 参数 |
描述 |
| index |
必需。规定从何处添加/删除元素。 |
| 该参数是开始插入和(或)删除的数组元素的下标,必须是数字。 |
? |
| howmany |
必需。规定应该删除多少元素。必须是数字,但可以是 "0"。 |
| 如果未规定此参数,则删除从 index 开始到原数组结尾的所有元素。 |
? |
| item1,...,itemX |
可选。要添加到数组的新元素 |
map()
语法:
map(function(currentValue,index,arr),thisValue)
参数:
![]()
?
![]()
?
运算符
算数运算符
# + - * / % ++ --
var x=10;
var res1=x++;
var res2=++x;
?
res1;
10
res2;
12
?
# 这里由于的x++和++x在出现赋值运算式,x++会先赋值再进行自增1运算,
# 而++x会先进行自增运算再赋值!
?
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>i=10,j=10;i+j=7</p>
<p id="sumid"></p>
<button onclick="mysum()">结果</button>
?
<script>
? ?function mysum() {
? ? ? ?var i = 10;
? ? ? ?var j = 10;
? ? ? ?var m = i + j;
? ? ? ?document.getElementById("sumid").innerHTML=m;
? }
</script>
</body>
</html>
?
比较运算符
> >= < <= != == === !==
?
注意
1 == “1” ?
逻辑运算符
&& || !
?
赋值运算符
= += -= *= /=
?
流程控制
if-else
var a = 10;
if (a > 5){
?console.log("yes");
}else {
?console.log("no");
}
?
if-else if-else
var a = 10;
if (a > 5){
?console.log("a > 5");
}else if (a < 5) {
?console.log("a < 5");
}else {
?console.log("a = 5");
}
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
? ?var i = 19;
? ?if (i >=10){
? ? ? ?document.write("我就喜欢i >= 10")
? }else if(i<10){
? ? ? ?document.write("为什么i<10")
? }else{
? ? ? ?document.write("i到底是多少?")
? }
</script>
</body>
</html>
?
switch
var day = new Date().getDay();
switch (day) {
?case 0:
?console.log("Sunday");
?break;
?case 1:
?console.log("Monday");
?break;
default:
?console.log("...")
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
? ?var i=5;
? ?switch (i) {
? ? ? ?case 1:
? ? ? ? ? ?document.write('i=1');
? ? ? ?case 2:
? ? ? ? ? ?document.write('i=2');
? ? ? ?default:
? ? ? ? ? ?
循环
for
for (var i=0;i<10;i++){
? ?console.log(i)
}
?
?
var a = ['aa','bb','cc'];
for (var i=0;i<a.length;i++){
? ?console.log(i);
? ?console.log(a[i]);
}
?
while
var i = 0;
while (i < 10) {
?console.log(i);
?i++;
}
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
函数
函数是由事件驱动或者当他被调用时执行的可重复使用的代码块.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?
函数定义
JavaScript中的函数和Python中的非常类似,只是定义方式有点区别
function 函数名() {
函数体; (代码块)
}
?
调用函数
函数在定义好之后,不能自动执行,需要进行调用.
在javascript中直接调用
调用方式: 在<script>标签内调用 在HTML文件中调用
sum(1,2); ?
?
通过HTML调用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?function demo() {
? ? ? ? ? ?var a = 10;
? ? ? ? ? ?var b = 20;
? ? ? ? ? ?var sum = a + b;
? ? ? ? ? ?alert(sum);
? ? ? }
? ?</script>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="demo()">求和</button>
</body>
</html>
?
补充: ES6中允许使用“箭头”(=>)定义函数。
var f = v => v;
// 等同于
var f = function(v){
?return v;
}
?
如果箭头函数不需要参数或需要多个参数,就是用圆括号代表参数部分:
var f = () => 5;
注意: 函数只能返回一个值,如果要返回多个值,只能将其放在数组或对象中返回.
带参数的函数
函数传参 在函数的调用中,也可以传递值,这些值称为参数
?
参数的个数可以为任意多,每个参数通过","隔开 参数在传递时,其顺序必须一致 参数意义: 通过传递参数的个数以及参数的类型不同完成不同的功能.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?function demo(a,b) {
? ? ? ? ? ?var sum = a + b;
? ? ? ? ? ?alert(sum)
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? ?function demo2(name,age) {
? ? ? ? ? ?alert("Hello:" + name + ",我的年龄是:" + age)
? ? ? }
? ?</script>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="demo2('alice',22)">点击</button>
</body>
</html>
?
带返回值的函数
返回值 有时,我们需要将函数的值返回给调用他的地方 通过return语句就可以实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?function demo() {
? ? ? ? ? ?return "Hello";
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?var v1=demo()+":youmen"
? ? ? ?alert(v1)
? ?</script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
匿名函数
?
?
函数的全局变量和局部变量
局部变量:
在JavaScript函数内部声明的变量(使用 var)是局部变量,所以只能在函数内部访问它(该变量的作用域是函数内部)。只要函数运行完毕,本地变量就会被删除。
全局变量:
在函数外声明的变量是全局变量,网页上的所有脚本和函数都能访问它。
变量生存周期:
JavaScript变量的生命期从它们被声明的时间开始。 局部变量会在函数运行以后被删除。 全局变量会在页面关闭后被删除。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?
异常捕获
异常 当JavaScript引擎执行JavaScript代码时,发生错误,导致程序停止运行. 异常抛出 当异常产生,并且将这个异常生成一个错误信息 异常捕获
定义异常
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
? ?var str="hello";
? ?function demo() {
? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ?alert(str)
? ? ? } catch (err) {
? ? ? ? ? ?alert(err)
? ? ? }
? }
? ?demo()
</script>
</body>
</html>
?
自定义异常
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form>
? ?<input id="txt" type="text">
? ?<input id="button" type="button" onclick="demo()" value="点我">
</form>
?
<script>
? ?function demo() {
? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ?var e = document.getElementById("txt").value;
? ? ? ? ? ?if (e == "") {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?throw "第一个用户输入异常为空";
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? } catch (err) {
? ? ? ? ? ?alert(err);
? ? ? }
? }
</script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
面向对象
在ES5中没有类的概念,只有个构造函数,命名的首字母要大写,实例化的时候使用New关键字进行实例化
?
在JavaScript中创建一个对象使用new这个关键字.
ES5中实现对象的方式
但是在定义一个类的时候不同的版本是不同的。 ES5 中,定义一个函数,并且这个函数名的首字母大写即可。 首字母大写是规则,不是必须的语法。
ES6中,可以使用class这个关键字
this 关键字相当于 python 中的 self, 不同的是在定义一个类方法时 this 关键字不是必须的参数。所以 this 一般总是用在定义变量和使用上变量上。
function Foo(name,age){
? ?this.Name = name;
? ?this.Age = age;
}
?
obj = new Foo('yangge',18)
obj.Name
?
?
function Foo(name,age){
? ?this.Name = name;
? ?this.Age = age;
? ?this.show = function(){
? ? ? ?alert(this.Name)
? }
}
?
obj = new Foo('yangge',18)
obj.Name
obj.show()
?
obj2 = new Foo('yangge',18)
obj2.show()
?
?
原型prototype
之前的方式会在每次创建实例的时候,函数是属于每个对象的,所以每次创建新对象的时候,函数都会被创建一次. 利用原型可以实现方法的重用,不论创建多少实例,方法不会每次都被重新创建.
function Foo(name,age){
? this.Name = name;
? this.Age = age;
}
?
Foo.prototype.show = function(){
? console.log(this.Name);
}
?
ES6中实现对象的方式: class
class Person {
? constructor(name,age) {
? ? ? this.name = name;
? ? ? this.age = age;
? }
?
? showName() {
? ? ? return this.name;
? }
}
?
var p1 = new Person("shark",18);
console.log(p1.showName())
?
constructor方法
类似python中的init constructor方法是类的默认方法,通过new命令生成对象实例时,自动调用该方法. 一个类必须有constructor方法,如果没有显式定义它,一个空的constructor方法会被默认添加. 其实和python差不多,语言都是相通的.
class Person {
}
?
// 等同于
class Person {
constructor(){}
}
# constructor方法默认返回实例对象(即this)
?
继承
class可以通过extends关键字实现继承
class Person {
? ?constructor(name,age) {
? ? ? ?this.name = name;
? ? ? ?this.age = age;
? }
?
? ?showName() {
? ? ? ?return ?this.name;
? }
}
?
class TeacherPerson extends Person {
? ?constructor(name,age,level) {
? ? ? ?super(name,age);
?
super关键字,它在这里表示父类的构造函数,用来新建父类的this对象。
?
子类必须在constructor方法中调用super方法,否则新建实例时会报错。这是因为子类自己的this对象,必须先通过父类的构造函数完成塑造,得到与父类同样的实例属性和方法,然后再对其进行加工,加上子类自己的实例属性和方法。如果不调用super方法,子类就得不到this对象。
?
时间(Date对象)
Example
# 浏览器console ?
?
Example2
<!DOCTYPE html> ?
<html lang="en"> ?
<head> ?
<meta charset="UTF-8"> ?
<title>Title</title> ?
</head> ?
<body> ?
<script> ?
var date=new Date(); ?
时钟操作
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body onload="startTime()">
<script>
? ?function startTime() {
? ? ? ?var today = new Date();
? ? ? ?var h = today.getHours();
? ? ? ?var m = today.getMinutes();
? ? ? ?var s = today.getSeconds();
? ? ? ?m = checkTime(m);
? ? ? ?s = checkTime(s);
? ? ? ?document.getElementById("timetxt").innerHTML = h + ":" + m + ":" + s;
? ? ? ?t = setTimeout(function () {
? ? ? ? ? ?startTime();
? ? ? },500);
? }
?
? ?function checkTime(i) {
? ? ? ?if (i < 10) {
? ? ? ? ? ?i = "0" + i;
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return i;
? }
</script>
?
<div id="timetxt"></div>
</body>
</html>
?
?
Json对象
var str1 = '{"name": "chao","age": 18}';
var obj1 = {"name": "chao","age": 18};
?
DOM事件
BOM(Browser Object Model)是指浏览器对象模型,它使 JavaScript 有能力与浏览器进行“对话”。
?
DOM (Document Object Model)是指文档对象模型,通过它,可以访问HTML文档的所有元素。
?
当网页被加载时,浏览器会创建页面的文档对象模型(DocumentObjectMode)
?
DOM操作HTML主要有四种方式
![]()
?
查找标签
和css一样,要想操作某个标签需要先找到它
直接查找
document.getElementById ? ? ? ? ?
?
Example1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="c1" id="d1">
? 待到将军归来日,朕与将军解战袍!
</div>
?
<div class="c1" id="d2">
? 日照香炉生紫烟,遥看瀑布挂前川.
</div>
<button class="btn" onclick="f1(this);">变</button>
?
?
<script>
? ?var btn = document.getElementsByClassName('btn')
? ?console.log(btn);
?
? ?function f1() {
? ? ? ?var a = document.getElementById('d1');
? ? ? ?a.innerText = '带到YouMen归来日!'
? }
</script>
</body>
</html>
?
间接查找
parentElement ? ? ? ? ?
?
Example
# 标签结构:
<a href="">更多古诗词</a>
?
<div class="cc">
?
? ?<div class="c1" id="d1">
? ? ? 待到将军归来日,朕与将军解战袍
? ?</div>
?
? ?<div class="c1" id="d2">
? ? ? 日照香炉生紫烟,遥看瀑布挂前川
? ?</div>
?
</div>
<button id="but" onclick="f1(this);">改变</button>
<span>这是span标签</span>
?
# 查询方式展示:
<script>
?
? ?var parent_ele = document.getElementsByClassName('cc');
? ?
?
节点操作
创建节点(标签)
语法:
createElement(标签名)
示例:
var a = document.createElement('a');
a.innerText = '百度';
"百度"
<a>百度</a>
?
?
添加节点
语法:
追加一个子节点(作为最后的子节点)
somenode.appendChild(newnode);
把增加的节点放到某个节点的前边。
somenode.insertBefore(newnode,某个节点);
示例:
删除节点
语法:
获得要删除的元素,通过父元素调用该方法删除。
somenode.removeChild(要删除的节点)
var d = document.getElementById('d');
var d1 = document.getElementById('d1');
d.removeChild(d1);
?
替换节点:
语法:
somenode.replaceChild(newnode,某个节点);
somenode是父级标签,然后找到这个父标签里面的要被替换的子标签,然后用新的标签将该子标签替换掉
var d = document.getElementById('d');
d1 = d.children[0];
var a = document.createElement('a');
a.innerText = '百度';
d.replaceChild(a,d1);
标签节点的操作都是基于先要找到父级标签,通过父级标签的相应功能进行操作。
?
?
DOM操作HTML
方法: getElementsByName() 获取name
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<p name="pn">Hello</p>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?function getName() {
? ? ? ? ? ?var count=document.getElementsByName("pn");
? ? ? ? ? ?alert(count.length);
? ? ? ? ? ?var p=count[0];
? ? ? ? ? ?p.innerHTML="World";
? ? ? ? ? ?
getElementsByTagName() 获取元素,和上面方法差不多 getAttribute() 获取元素属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<a id="aid" title="得到了a标签的属性">Hello</a>
? ?<a id="aid2" onclick="setAttr()">World</a>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?function getAttr() {
? ? ? ? ? ?var anode=document.getElementById("aid");
? ? ? ? ? ?var attr = anode.getAttribute("title");
? ? ? ? ? ?alert(attr);
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? ?function setAttr() {
? ? ? ? ? ?var anode=document.getElementById("aid2");
? ? ? ? ? ?anode.setAttribute("title","动态设置a的title属性");
? ? ? ? ? ?var attr=anode.getAttribute("title");
? ? ? ? ? ?alert(attr);
? ? ? }
? ?</script>
</body>
</html>
?
childNodes()
?
?
1.改变HTML输出流
注意: 绝对不要在文档加载完成之后使用document.write(),这会覆盖该文档.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello</p>
<p>Hello</p>
<p>Hello</p>
<p>Hello</p>
<button onclick="demo()">点我</button>
<script>
? function demo() {
? ? ? document.write("World");
? }
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.寻找元素
通过id找到HTML元素 通过标签名找到HTML元素
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<p id="pid">Hello</p>
? ?<button onclick="demo()">点我</button>
?
<script>
? ?function demo() {
? ? ? ?document.getElementById("pid").innerHTML="W";
? ? ? ?document.getElementsByClassName("p");
3.改变HTML内容
使用属性: innerHTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<img id="imgid" src="1.jpg">
? ?<button onclick="demo2()">图片</button>
?
? ?<a id="aid" href="http://www.baidu.com">百度一下</a>
? ?<button onclick="demo()">点我</button>
?
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?function demo() {
? ? ? ? ? ?document.getElementById("aid").href="http://www.weibo.com";
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? ?function demo2() {
? ? ? ? ? ?document.getElementById("imgid").src="2.jpg";
? ? ? }
? ?</script>
</body>
</html>
?
DOM操作CSS
document.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
? ?<style>
? ? ? ?.div{
? ? ? ? ? ?width: 100px;
? ? ? ? ? ?height: 100px;
? ? ? ? ? ?background-color: darkgray;
? ? ? }
? ?</style>
</head>
<body>
? ?<div id="div" class="div">
? ? ? Hello
? ?</div>
?
? ?<button onclick="demo()">按钮</button>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?function demo() {
? ? ? ? ? ?document.getElementById("div").style.background="red";
? ? ? ? ? ?document.getElementById("div").style.color="green";
? ? ? }
? ?</script>
</body>
</html>
DOM事件句柄
Example1
<!DOCTYPE html> ?
<html lang="en"> ?
<head> ?
<meta charset="UTF-8"> ?
<title>Title</title> ?
</head> ?
<body> ?
<p id="div">Hello</p> ?
<button id="btn">按钮</button> ?
<script> ?
document.getElementById("btn").addEventListener("click",function () { ?
alert("hello") ?
} ?
) ?
</script> ?
</body> ?
</html> ?
Example2
<!DOCTYPE html> ?
<html lang="en"> ?
<head> ?
<meta charset="UTF-8"> ?
<title>Title</title> ?
</head> ?
<body> ?
<button id="btn">按钮</button> ?
<script> ?
var x = document.getElementById("btn"); ?
x.addEventListener("click",hello); ?
事件流
事件流
描述的是在页面中接受事件的顺序
事件冒泡
是由具体的元素接受,然后逐级向上传播至最不具体的元素的节点(文档)
事件捕获
最不具体的节点先接受事件,而最具体的节点应该是最后接受事件.
事件处理
HTML事件处理 直接添加到HTML结构中
DOM事件处理 把一个函数赋值给一个事件处理程序属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div">
? <button id="btn1" onclick="demo()">点我</button>
</div>
?
<!-- ? <script>-->
<!-- ? ? ? function demo() {-->
<!-- ? ? ? ? ? alert("Hello,html事件处理")-->
<!-- ? ? ? }-->
<!-- ? </script>-->
?
<script>
? var btn1 = document.getElementById("btn1"); //如果有多个后面会覆盖前面的
? btn1.onclick = function () {alert("Hello DOM0级事件处理程序")};
? btn1.onclick=null;
</script>
</body>
</html>
DOM2级事件处理 addEventListener("事件名","事件处理函数","布尔值"); true: 事件捕获 false: 事件冒泡 removeEventListener();
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? <button id="btn1">点我</button>
? <script>
? ? ? document.getElementById("btn1").addEventListener("click",showType);
? ? ? function showType(event) {
? ? ? ? ? alert(event.type);
? ? ? ? ? alert(event.target);
? ? ? }
? </script>
</body>
</html>
IE事件处理程序 attachEvent detachEvent
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<button id="btn1">点我</button>
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?document.getElementById("btn1").addEventListener("click",showType);
? ? ? ?document.getElementById("div").addEventListener("click",showDiv);
? ? ? ?function showType(event) {
? ? ? ? ? ?alert(event.type);
? ? ? ? ? ?alert(event.target);
? ? ? ? ? ?event.stopPropagation();
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
8.5 作用域: 其他语言: 以代码块作为作用域
public void Func() {
if (1==1) {
string name = 'Java';
}
console.writeline(name);
}
Func()
// 报错,string name变量只在那个代码块起作用.
Python 以函数作为作用域
# 情况一
def fun():
if 1 == 1:
name = 'alice'
print(name)
func()
?
# 情况二:
def func():
if i ==1
name = 'alice'
print(name)
func()
print(name)
//报错
JavaScript: 以函数作为作用域
function func(){
? if(1==1){
? ? ? var name='alice';
? }
? console.log(name);
}
?
func()
VM1096:5 alice
?
JavaScript作用域总结 1.JavaScript是以函数为作用域 2.函数的作用域在函数未被调用之前,已经创建 3.函数的作用域存在作用域链,并且也是在调用之前创建 4. 函数内部变量提前声明
8.4 序列化
JSON.stringify() # 将对象转换为字符串
JSON.parse() # 将字符串转换为对象类型
?
# 客户端(cookie) => 服务器端
# 将数据经过转义后,保存在cookie
?
# 浏览器Console输入下面demo
url = "https://www.sogou.com/web?query=理解";
"https://www.sogou.com/web?query=理解"
url
"https://www.sogou.com/web?query=理解"
encodeURI(url)
"https://www.sogou.com/web?query=%E7%90%86%E8%A7%A3"
newUrl = encodeURI(url)
"https://www.sogou.com/web?query=%E7%90%86%E8%A7%A3"
decodeURI(newUrl)
"https://www.sogou.com/web?query=理解"
newUrl = encodeURIComponent(url)
"https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sogou.com%2Fweb%3Fquery%3D%E7%90%86%E8%A7%A3"
?
eval以及时间操作 eval
# python:
# val = eval(表达式)
# exec(执行代码,没有返回值)
?
# JavaScript:
eval(集成了上面两个功能)
BOM对象
windows对象
windows对象是BOM的核心,windows对象是指当前的浏览器窗口 所有JavaScript全局对象,函数以及变量均自动成为windows对象的成员. 全局变量是window对象的属性 全局函数是windows对象的方法 甚至HTML DOM的document也是window对象的属性之一
?
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn" onclick="btnClicked()">点我</button>
?
<script>
? ?function btnClicked() {
? ? ? ?window.open("index.html","windowname","height=200,width=200,top=100,left=100,toolbar=no,menubar=no")
? ? ? ?window.close();
? }
</script>
</body>
</html>
计时器对象
通过使用JavaScript,我们有能力做到在一个设定的时间间隔之后来执行代码,而不是在函数被调用后立即执行,我们称之为计时事件.
?
计时方法: setInterval() 间隔指定的毫秒数不停地执行指定的代码 clearInterval()方法用于停止setInterval()方法执行的函数代码
?
setTimeout() 暂停指定毫秒数后执行指定的代码 clearTimeout()方法用于停止执行setTimeout()方法的函数代码
# var t = setTimeout("js语句",毫秒) 第一个参数js语句多数是写一个函数,不然一般的Js语句到这里直接执行了,
# 先用函数封装一下,返回值t就是一个ID值(浏览器自动给你分配的)
# setTimeout() 方法会返回某个值。在上面的语句中,值被储存在名为 t 的变量中。假如你希望取消这个 setTimeout(),你可以使用这个变量名来指定它。
?
# setTimeout() 的第一个参数是含有 JavaScript 语句的字符串。这个语句可能诸如 "alert('5 seconds!')",或者对函数的调用,诸如 alertMsg()"。
?
# 第二个参数指示从当前起多少毫秒后执行第一个参数(1000 毫秒等于一秒)。
setTimeout(function(){alert("xxx")},2000)
?
?
setInterval()
每隔一段时间做一些事情
# setInterval() 方法可按照指定的周期(以毫秒计)来调用函数或计算表达式。
?
# setInterval() 方法会不停地调用函数,直到 clearInterval() 被调用或窗口被关闭。由 setInterval() 返回的 ID 值可用作 clearInterval() 方法的参数。
?
# 语法
# setInterval("js语句",时间间隔)
?
# 返回值
# 一个可以传递给Windows.clearInterval(),从而取消对code的周期性执行的值.
?
clearInterval()
# clearInterval() 方法可取消由 setInterval() 设置的 timeout。
?
# clearInterval() 方法的参数必须是由 setInterval() 返回的 ID 值。
?
# 语法:
# clearInterval(setinterval返回的ID值)
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn" onclick="stopWin()">暂停</button>
<p id="ptime"></p>
?
<script>
? ?
?
Navigator对象
navigator.appName
?
?
Histoy对象
History对象 window.history 对象包含浏览器的历史(url)的集合
?
HIstory_Demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- ? <a href="index.html">按钮</a>-->
<!-- ? <button id="btn" onclick="goob()">按钮</button>-->
?
<!-- ? <script>-->
<!-- ? ? ? function goob() {-->
<!-- ? ? ? ? ? history.forward();-->
<!-- ? ? ? }-->
<!-- ? </script>-->
?
? <a href="index.html">登录</a>
</body>
</html>
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? <form>
? ? ? <input type="text" id="username">
? ? ? <button id="btn" onclick="safe()">登录</button>
? </form>
?
? <script>
? ? ? function safe() {
? ? ? ? ? var name=document.getElementById("username").value;
? ? ? ? ? if(name=="youmen"){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? history.go(-1);
? ? ? ? ? }else{
? ? ? ? ? ? ? alert("输入错误");
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? </script>
</body>
</html>
location对象
window.location对象用于获取当前页面的地址,并把浏览器重定向到新的页面
?
?
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn" onclick="getLoc()">点击</button>
<p id="ptime"></p>
<script>
? ?function getLoc() {
? ? ? ?document.getElementById("ptime").innerHTML = window.location.port;
? ? ? ?document.getElementById("ptime").innerHTML = window.location.protocol;
? ? ? ?document.getElementById("ptime").innerHTML = window.location.hostname;
? ? ? ?document.getElementById("ptime").innerHTML = window.location.pathname;
? }
</script>
?
<script>
? ?function getLoc2() {
? ? ? ?location.assign("http://www.baidu.com");
? }
</script>
</body>
</html>
Screen对象
主要做屏幕适配,windows.screen对象包含有关用户屏幕的信息 属性
?
?
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? <button id="btn" onclick="getLoc()">按钮</button>
? <p id="ptime"></p>
?
? <script>
? ? ? document.write("可用高度:"+screen.availHeight+",可用宽度:"+screen.availWidth);
? ? ? document.write("高度"+screen.height+",宽度:"+screen.width);
? </script>
</body>
</html>
?
DOM和BOM选择器
JavaScript分为ECMAScript,DOM,BOM BOM(Browser Objuct Model) 是指浏览器对象模型,它使JavaScript有能力与浏览器进行‘对话’. DOM(Document Object Model)是指文档对象模型,通过他,可以访问HTML文档的所有元素. Window对象是客户端JavaScript最高层对象之一,由于window对象是其它大部分对象的共同祖先,在调用window对象的方法和属性时,可以省略window对象的引用。例如:window.document.write()可以简写成:document.write()。
windows对象
所有浏览器都支持 window 对象。它表示浏览器窗口。 如果文档包含框架(frame 或 iframe 标签),浏览器会为 HTML 文档创建一个 window 对象,并为每个框架创建一个额外的 window 对象。 没有应用于 window 对象的公开标准,不过所有浏览器都支持该对象。 所有 JavaScript 全局对象、函数以及变量均自动成为 window 对象的成员。 全局变量是 window 对象的属性。全局函数是 window 对象的方法。 接下来要讲的HTML DOM 的 document 也是 window 对象的属性之一。
一般常用的window方法:
* window.innerHeight - 浏览器窗口的内部高度
* window.innerWidth - 浏览器窗口的内部宽度
* window.open() - 打开新窗口
* window.close() - 关闭当前窗口
windows的子对象 navigator对象
浏览器对象,通过这个对象可以判定用户所使用的浏览器,包含了浏览器相关信息.
navigator.appName // Web浏览器全称
navigator.appVersion // Web浏览器厂商和版本的详细字符串
navigator.userAgent // 客户端绝大部分信息
navigator.platform // 浏览器运行所在的操作系统
screen对象
屏幕对象,不常用
一些属性
screen.availWidth - 可用的屏幕宽度
screen.availHeight - 可用的屏幕高度
history对象(了解即可)
window.history 对象包含浏览器的历史。
浏览器历史对象,包含了用户对当前页面的浏览历史,但我们无法查看具体的地址,可以简单的用来前进或后退一个页面.
history.forward() // 前进一页
history.back() // 后退一页
location对象
window.location 对象用于获得当前页面的地址 (URL),并把浏览器重定向到新的页面。 常用属性和方法:
location.href 获取URL
location.href="URL" // 跳转到指定页面
location.reload() 重新加载页面
11.2 Dom 1. 直接找到标签
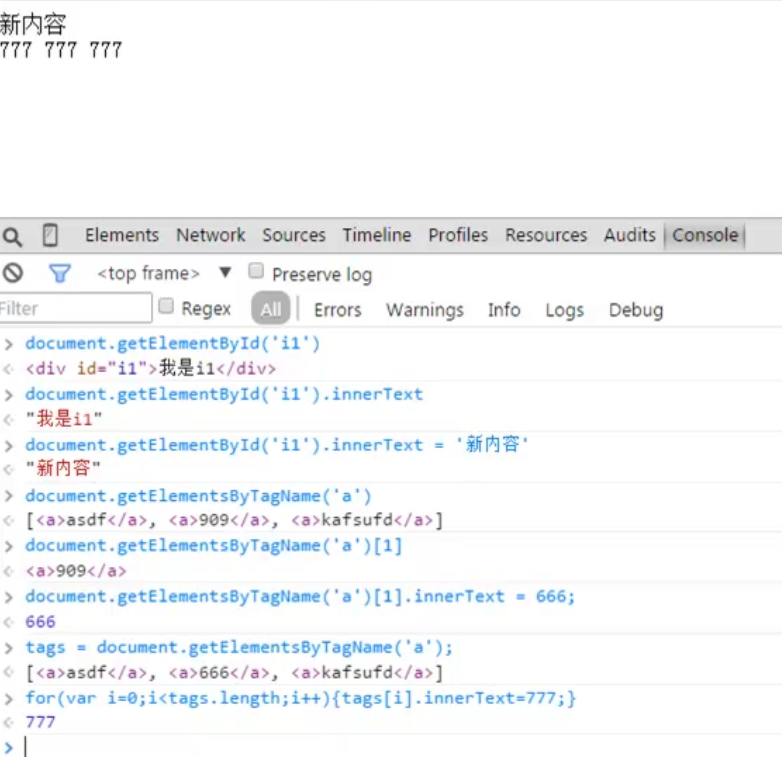
# 获取单个元素 ? document.getElementById('i1') ? 根据ID获取一个标签
# 获取多个元素(列表) ? document.getElementsByTagName('div') 根据name属性获取标签集合
# 获取多个元素(列表) ? document.getElementClassName('c1') ? 根据class属性获取标签集合
# document.getElementsByTagName ? 根据标签名获取标签集合
?
?
# 2. 操作标签
# 获取标签中的文本内容
# 标签.innerText
?
# 对标签内部文本
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? <div id="i1">
? ? ? 我是i1
? </div>
?
? <a>YouMen1</a>
? <a>YouMen2</a>
? <a>YouMen3</a>
</body>
</html>
2.间接找到标签
tag = document.getElementById('i1')
?
parentElement //父节点标签元素
children //所有子标签
firstElementChild //第一个子标签元素
lastElementChild //最后一个子标签元素
nextElementtSibling //下一个兄弟标签元素
previousElementSibling// 上一个兄弟标签元素
3.操作标签 a. innerText
> 获取标签中的文本内容
> 标签. innerText
?
> 对标签内部文本进行重新复制
> innerText = ""
b className
# tag.className = 》 直接整体做操作
# tag.classList.add('样式名') ? 添加指定样式
# tag.classList.remove('样式名') 删除指定样式.
?
# ps:
<div onclick = 'func();;'>点我</div>
<script>
function func(){
?
}
</script>
?
# checkbox
# 获取值
# checkbox对象.checked
# 设置值
# checkbox对象.checked=true
属性操作
# attributes
# getAttribute
# removeAttribute
创建标签,并添加到HTML中 有两种创建方式,字符串和对象方式 Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? <input type="button" onclick="AddEle1();" value="+" />
?
? <input type="button" onclick="AddEle2();" value="+" />
? <div id="i1">
? ? ? <p><input type="text" /></p>
? </div>
?
? <script>
? ? ? function AddEle1() {
? ? ? // 创建一个标签,将标签添加到i1里面.
? ? ? ? ? var tag = "<p><input type='text' /></p>"
? ? ? ? ? document.getElementById('i1').insertAdjacentHTML("beforeEnd",tag);
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? function AddEle2() {
? ? ? ? ? // 对象方式创建
? ? ? ? ? var tag = document.createElement('input');
? ? ? ? ? tag.setAttribute("type",'text');
? ? ? ? ? tag.style.fontSize = '16px';
? ? ? ? ? tag.style.color = 'red';
?
? ? ? ? ? var p = document.createElement('p');
? ? ? ? ? p.appendChild(tag);
?
? ? ? ? ? document.getElementById('i1').appendChild(p);
? ? ? }
? </script>
</body>
</html>

提交表单 任何标签都可以通过DOM提交表单
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? <form id="f1" action="http://www.baidu.com">
? ? ? <input type="text" />
? ? ? <input type="submit" value="提交" />
? ? ? <a onclick="submitForm();">提交吧</a>
? </form>
?
? <script>
? ? ? function submitForm(){
? ? ? ? ? // document.getElementById('f1').submit();
? ? ? ? ? // alert('1234')
? ? ? ? ? // var v = confirm("真的要删除吗?");
? ? ? ? ? // console.log(v)
? ? ? ? ? // 会根据提示信息确定和取消对应true/false
? ? ? ? ? // var obj = setInterval(function () {
? ? ? ? ? // ? ? console.log(1);
? ? ? ? ? // },1000); //定时器
? ? ? ? ? // clearInterval(obj) //清除定时器
? ? ? ? ? // setTimeout(function () { // 一定时间后执行“一次”.删除邮箱提示二秒消失
? ? ? ? ? // ? ? console.log('timeout');
? ? ? ? ? // },5000);
? ? ? }
? </script>
</body>
</html>
Example setTimeout
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? <div id="status"></div>
? <input type="button" value="删除" onclick="DeleteEle();" />
?
? <script>
? ? ? function DeleteEle() {
? ? ? ? ? document.getElementById('status').innerText = "已删除"
? ? ? ? ? setTimeout(function () {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? document.getElementById('status').innerText = "";
? ? ? ? ? },3000);
? ? ? }
? </script>
</body>
</html>
弹出框,重定向等
alert(123);
location.href = "" # 重定向,跳转
location.reload() # 页面刷新
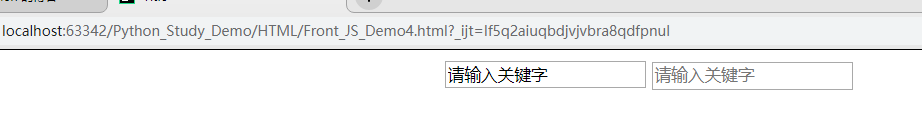
Dom Example1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? <div style="width: 600px;margin: 0 auto;">
? ? ? <input id="i1" onblur="Blur();" onfocus="Focus();" type="text" value="请输入关键字" />
?
? ? ? <!--<input type="text " placeholder="请输入关键字"> 仅支持最新浏览器-->
? </div>
?
? <script>
? ? ? function Focus() {
? ? ? ? ? var tag = document.getElementById('i1');
? ? ? ? ? var val = tag.value;
? ? ? ? ? if(val == "请输入关键字"){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? tag.value="";
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? ? ? function Blur() {
? ? ? ? ? var tag = document.getElementById('i1');
? ? ? ? ? var val = tag.value;
? ? ? ? ? if(val.length == 0){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? tag.value = "请输入关键字";
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? </script>
</body>
</html>
提交事件
# 绑定事件两种方式
# 直接标签绑定 onclick='xxx()' onfocus
# 先获取Dom对象,然后进行绑定
document.getElementById('xx').onclick
document.getElementById('xx').onfocus
?
this,当前触发事件的标签
# 第一种绑定方式
# <input id = 'i1' type='button' onclick='ChickOn(this)'>
function ClickOn(self) {
// self 当前点击的标签
}
?
# 第二种绑定方式
<input id = 'i1' type='button' >
document.getElementById('i1').onclick = function() {
// this 代表当前点击的标签
}
?
事件
事件是可以被JavaScript侦测到的行为
| 事件 |
描述 |
| onClick |
点击事件 |
| onMouSEOver |
鼠标经过事件 |
| onMouSEOut |
鼠标移除事件 |
| onChange |
文本内容改变事件 |
| onSelect |
文本框选中事件 |
| onFocus |
光标聚集事件 |
| onBlur |
移开光标事件 |
| onLoad |
网页加载事件 |
| onUnload |
关闭网页事件 |
onclick ? ? ? ?当用户点击某个对象时调用的事件句柄。
ondblclick ? ? 当用户双击某个对象时调用的事件句柄。
?
onfocus ? ? ? ?元素获得焦点。 ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
?
绑定方式
方式一:(已经不常用了,多数用方式二了)
<div id="d1" onclick="changeColor(this);">点我</div> ?
<script> ?
?function changeColor(ths) { ?
? ?ths.style.backgroundColor="green";
}
</script>
?
?
方式二
<div id="d2">点我</div>
<script>
?var divEle2 = document.getElementById("d2");
?divEle2.onclick=function () {
?
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
? ?<style>
? ? ? ?#d {
? ? ? ? ? ?width: 200px;
? ? ? ? ? ?height: 200px;
? ? ? ? ? ?background-color: #7e55ff;
? ? ? ? ? ?border-radius: 50%;
? ? ? }
? ?</style>
</head>
<body>
? ?<button id="btn">单击</button>
? ?<div id="d"></div>
?
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?var btn = document.getElementById('btn');
? ? ? ?btn.onclick = function () {
? ? ? ? ? ?this.style.display = 'none';
? ? ? ? ? ?var d = document.getElementById('d')
? ? ? ? ? ?d.style.backgroundColor = 'red';
? ? ? }
? ?</script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
一个简单的事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? <button onclick="demo()">按钮</button>
? <script>
? ? ? function demo() {
? ? ? ? ? alert("Hello")
? ? ? }
? </script>
</body>
</html>
?
鼠标经过和移出的效果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
? ?<style>
? ? ? ?div{
? ? ? ? ? ?width: 100px;
? ? ? ? ? ?height: 100px;
? ? ? ? ? ?background-color: #7e55ff;
? ? ? }
? ?</style>
</head>
<body>
? ?<div class="div" onmouSEOut="onOut(this)" onmouSEOver="onOver(this)"></div>
? ?
?
?
输入框被改变就提示信息
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<form>
? ? ? ?<input type="text" onchange="changeDemo()">
? ?</form>
?
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?function changeDemo() {
? ? ? ? ? ?alert("Hello,内容改变了")
? ? ? }
? ?</script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
文本选中事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?<form>
? ? ? ?<input type="text" onselect="change(this)">
? ?</form>
? ?
?
?
光标选中事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
? ?
?
?
?
网页加载完毕事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? ?<meta charset="UTF-8">
? ?<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body onload="mgs()">
? ?<script>
? ? ? ?function mgs() {
? ? ? ? ? ?alert("网页加载完毕");
? ? ? }
? ?</script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
弹出框
可以在 JavaScript 中创建三种消息框:警告框、确认框、提示框
警告框
警告框经常用于确保用户可以得到某些信息。
当警告框出现后,用户需要点击确定按钮才能继续进行操作。
alert("弹出信息")
?
确认框
确认框用于使用户可以验证或者接受某些信息。
当确认框出现后,用户需要点击确定或者取消按钮才能继续进行操作。
如果用户点击确认,那么返回值为 true。如果用户点击取消,那么返回值为 false。
语法:
confirm("你确定吗")
true
?
?
提示框
提示框经常用于提示用户在进入页面前输入某个值。
当提示框出现后,用户需要输入某个值,然后点击确认或取消按钮才能继续操纵。
如果用户点击确认,那么返回值为输入的值。如果用户点击取消,那么返回值为默认值,就是第二个参数,如果没有默认值那么返回null。
语法:
prompt("请在下方输入","您的答案")
"您的答案: 1234"
?
常见小案例
省市
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
?<meta charset="UTF-8">
?<meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=edge">
?<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
?<title>select联动</title>
</head>
<body>
<select id="province">
?<option>请选择省:</option>
</select>
?
<select id="city">
?<option>请选择市:</option>
</select>
?
<script>
?data = {"河北省": ["廊坊","邯郸"],"北京": ["朝阳区","海淀区"],"山东": ["威海市","烟台市"]};
?
?var p = document.getElementById("province");
?var c = document.getElementById("city");
?
?
?
后台布局案例
js实线瀑布流效果
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<script src="js/waterfall.js"></script>
<style type="text/css">
? *{padding: 0;margin:0;}
? #main{
? ? ? position: relative;
? }
? .pin{
? ? ? padding: 15px 0 0 15px;
? ? ? float:left;
? }
? .box{
? ? ? padding: 10px;
? ? ? border:1px solid #ccc;
? ? ? box-shadow: 0 0 6px #ccc;
? ? ? border-radius: 5px;
? }
? .box img{
? ? ? width:162px;
? ? ? height:auto;
? }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="main">
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/1.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/2.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/3.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/4.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/5.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/6.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/7.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/8.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/9.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/10.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
? <div class="pin">
? ? ? <div class="box">
? ? ? ? ? <img src="./images/11.jpg"/>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
waterfall.js
window.onload=function(){
?
? waterfall('main','pin');
?
? var dataInt={'data':[{'src':'1.jpg'},{'src':'2.jpg'},{'src':'3.jpg'},{'src':'4.jpg'}]};
?
? window.onscroll=function(){
? ? ? if(checkscrollside()){
? ? ? ? ? var oParent = document.getElementById('main');// 父级对象
? ? ? ? ? for(var i=0;i<dataInt.data.length;i++){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? var oPin=document.createElement('div'); //添加 元素节点
? ? ? ? ? ? ? oPin.className='pin'; ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? //添加 类名 name属性
? ? ? ? ? ? ? oParent.appendChild(oPin); ? ? ? ? ? ? //添加 子节点
? ? ? ? ? ? ? var oBox=document.createElement('div');
? ? ? ? ? ? ? oBox.className='box';
? ? ? ? ? ? ? oPin.appendChild(oBox);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? var oImg=document.createElement('img');
? ? ? ? ? ? ? oImg.src='./images/'+dataInt.data[i].src;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? oBox.appendChild(oImg);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? waterfall('main','pin');
? ? ? };
? }
}
?
/*
? parend 父级id
? pin 元素id
*/
function waterfall(parent,pin){
? var oParent=document.getElementById(parent);// 父级对象
? var aPin=getClassObj(oParent,pin);// 获取存储块框pin的数组aPin
? var iPinW=aPin[0].offsetWidth;// 一个块框pin的宽
? var num=Math.floor(document.documentElement.clientWidth/iPinW);//每行中能容纳的pin个数【窗口宽度除以一个块框宽度】
? oParent.style.cssText='width:'+iPinW*num+'px;margin:0 auto;';//设置父级居中样式:定宽+自动水平外边距
?
? var pinHArr=[];//用于存储 每列中的所有块框相加的高度。a
? for(var i=0;i<aPin.length;i++){//遍历数组aPin的每个块框元素
? ? ? var pinH=aPin[i].offsetHeight;
? ? ? if(i<num){
? ? ? ? ? pinHArr[i]=pinH; //第一行中的num个块框pin 先添加进数组pinHArr
? ? ? }else{
? ? ? ? ? var minH=Math.min.apply(null,pinHArr);//数组pinHArr中的最小值minH
? ? ? ? ? var minHIndex=getminHIndex(pinHArr,minH);
? ? ? ? ? aPin[i].style.position='absolute';//设置绝对位移
? ? ? ? ? aPin[i].style.top=minH+'px';
? ? ? ? ? aPin[i].style.left=aPin[minHIndex].offsetLeft+'px';
? ? ? ? ? //数组 最小高元素的高 + 添加上的aPin[i]块框高
? ? ? ? ? pinHArr[minHIndex]+=aPin[i].offsetHeight;//更新添加了块框后的列高
? ? ? }
? }
}
?
? /*
? *通过父级和子元素的class类 获取该同类子元素的数组
? */
function getClassObj(parent,className){
? var obj=parent.getElementsByTagName('*');//获取 父级的所有子集
? var pinS=[];//创建一个数组 用于收集子元素
? for (var i=0;i<obj.length;i++) {//遍历子元素、判断类别、压入数组
? ? ? if (obj[i].className==className){
? ? ? ? ? pinS.push(obj[i]);
? ? ? }
? };
? return pinS;
}
/****
? *获取 pin高度 最小值的索引index
? */
function getminHIndex(arr,minH){
? for(var i in arr){
? ? ? if(arr[i]==minH){
? ? ? ? ? return i;
? ? ? }
? }
}
?
?
function checkscrollside(){
? var oParent=document.getElementById('main');
? var aPin=getClassObj(oParent,'pin');
? var lastPinH=aPin[aPin.length-1].offsetTop+Math.floor(aPin[aPin.length-1].offsetHeight/2);//创建【触发添加块框函数waterfall()】的高度:最后一个块框的距离网页顶部+自身高的一半(实现未滚到底就开始加载)
? var scrollTop=document.documentElement.scrollTop||document.body.scrollTop;//注意解决兼容性
? var documentH=document.documentElement.clientHeight;//页面高度
? return (lastPinH<scrollTop+documentH)?true:false;//到达指定高度后 返回true,触发waterfall()函数
}
?
Example1.Example1 模态对话框、全选、反选、取消
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
? <style>
? ? ? .hide{
? ? ? ? ? display: none;
? ? ? }
? ? ? .c1{
?
? ? ? ? ? position: fixed;
? ? ? ? ? left: 0;
? ? ? ? ? top: 0;
? ? ? ? ? right: 0;
? ? ? ? ? bottom: 0;
? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? opacity: 0.5;
? ? ? ? ? z-index: 9;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .c2{
? ? ? ? ? width: 500px;
? ? ? ? ? height: 400px;
? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? position: fixed;
? ? ? ? ? left: 50%;
? ? ? ? ? top: 50%;
? ? ? ? ? margin-left: -250px;
? ? ? ? ? margin-top: -200px;;
? ? ? ? ? z-index: 10;
? ? ? }
? </style>
</head>
<body style="margin: 0;">
? <div>
? ? ? <input type="button" value="添加" onclick="ShowMode();" />
? ? ? <input type="button" value="全选" onclick="SelectAll();" />
? ? ? <input type="button" value="取消" onclick="Cancel();" />
? ? ? <input type="button" value="反选" onclick="ReverseElection();" />
?
? ? ? <table>
? ? ? ? ? <thead>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? <tr>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <th>选择</th>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>主机名</td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>端口</td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? </tr>
? ? ? ? ? </thead>
? ? ? ? ? <tbody id="tb">
?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? <tr>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <input type="checkbox" />
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? </td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>1.1.1.1</td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>180</td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? </tr>
?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? <tr>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <input type="checkbox" id="test" />
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? </td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>1.1.1.2</td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>181</td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? </tr>
?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? <tr>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <input type="checkbox" />
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? </td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>1.1.1.3</td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <td>183</td>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? </tr>
? ? ? ? ? </tbody>
? ? ? </table>
? </div>
?
? <!--遮罩层开始-->
? <div id="i1" class="c1 hide"></div>
? <!--遮罩层结束-->
?
? <!--弹出框开始-->
? <div id="i2" class="c2 hide">
? ? ? <p><input type="text" /></p>
? ? ? <p><input type="text" /></p>
? ? ? <p>
? ? ? ? ? <input type="button" value="取消" onclick="Cancel()" />
? ? ? ? ? <input type="button" value="确定" />
? ? ? </p>
? </div>
? <!--弹出窗结束-->
?
? <script>
? ? ? function ShowMode() {
? ? ? ? ? document.getElementById('i1').classList.remove('hide');
? ? ? ? ? document.getElementById('i2').classList.remove('hide');
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? function SelectAll() {
? ? ? ? ? var tbody = document.getElementById('tb');
? ? ? ? ? //获取所有的tr
? ? ? ? ? var tr_list = tbody.children;
? ? ? ? ? for (var i=0;i<tr_list.length;i++){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? // 循环所有的tr,current_tr
? ? ? ? ? ? ? var current_tr=tr_list[i];
? ? ? ? ? ? ? var checkbox = current_tr.children[0].children[0];
? ? ? ? ? ? ? checkbox.checked=true
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? ? ? function Cancel() {
?
? ? ? ? ? var tbody = document.getElementById('tb');
? ? ? ? ? //获取所有的tr
? ? ? ? ? var tr_list = tbody.children;
? ? ? ? ? for(var i=0;i<tr_list.length;i++){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? //循环所有的tr,current_tr
? ? ? ? ? ? ? var current_tr = tr_list[i];
? ? ? ? ? ? ? var checkbox = current_tr.children[0].children[0];
? ? ? ? ? ? ? checkbox.checked = false;
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? document.getElementById('i1').classList.add('hide');
? ? ? ? ? document.getElementById('i2').classList.add('hide');
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? function ReverseElection() {
? ? ? ? ? var tbody = document.getElementById('tb')
? ? ? ? ? //获取所有的tr
? ? ? ? ? var tr_list = tbody.children;
? ? ? ? ? for (var i=0;i<tr_list.length;i++){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? var current_tr = tr_list[i];
? ? ? ? ? ? ? var checkbox = current_tr.children[0].children[0];
? ? ? ? ? ? ? if (checkbox.checked) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? checkbox.checked = false;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } else {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? checkbox.checked = true;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? </script>
</body>
</html>

Example2 后台管理布局1
后台管理布局: ?
# position: ?
# fiexd ----永远固定在窗口的某个位置 ?
# relative ----单独无意义 ?
# absolute ----第一次定位,可以在指定位置,滚轮滚动时,不在了
?
a.
# 左侧菜单跟滚动条
?
?
b.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
? <style>
? ? ? body{
? ? ? ? ? margin: 0;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .left{
? ? ? ? ? float: left;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .right{
? ? ? ? ? float: right;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header{
? ? ? ? ? height: 36px;
? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? color: white;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-content .menu{
? ? ? ? ? position: fixed;
? ? ? ? ? top: 36px;
? ? ? ? ? right: 0;
? ? ? ? ? left: 0;
? ? ? ? ? bottom: 0;
? ? ? ? ? width: 200px;
? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? /*min-width: 200px;*/
? ? ? ? ? /* ? 当20%小于200像素,就应用最小限制200像素*/
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-content .content{
? ? ? ? ? position: fixed;
? ? ? ? ? top: 36px;
? ? ? ? ? right: 0;
? ? ? ? ? bottom: 0;
? ? ? ? ? left: 200px;
? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? /*加上此行即可出现滚动条*/
? ? ? ? ? overflow: auto;
? ? ? }
?
? </style>
</head>
<body>
? <div class="pg-header"></div>
?
? <div class="pg-content">
? ? ? <div class="menu left">YouMen</div>
? ? ? <div class="content left">
? ? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p> ? ? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p> ? ? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p> ? ? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p> ? ? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p> ? ? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMen</p>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
?
? <div class="pg-footer"></div>
</body>
</html>

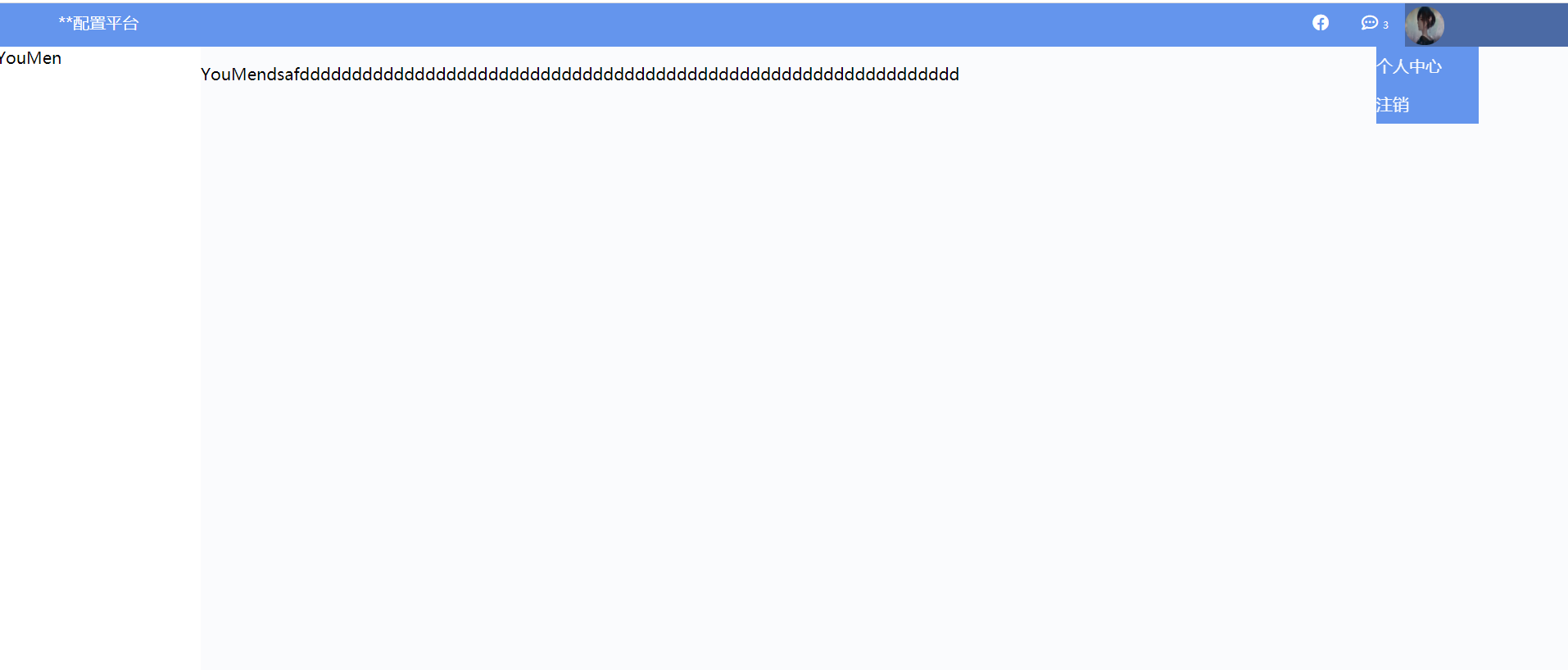
后台管理布局二
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
? <meta charset="UTF-8">
? <title>Title</title>
? <link rel="stylesheet" href="fontawesome-free-5.12.0-web/css/all.css">
? <style>
? ? ? body{
? ? ? ? ? margin: 0;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .left{
? ? ? ? ? float: left;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .right{
? ? ? ? ? float: right;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header{
? ? ? ? ? height: 42px;
? ? ? ? ? font-family: var(--monospace); position: relative; display: inline-block;"> CornflowerBlue;
? ? ? ? ? /*头部字体颜色*/
? ? ? ? ? color: white;
? ? ? ? ? /*让header里面文字上下居中*/
? ? ? ? ? line-height: 38px;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header .logo{
? ? ? ? ? width: 200px;
? ? ? ? ? font-family: var(--monospace); position: relative; display: inline-block;"> CornflowerBlue;
? ? ? ? ? /*让字体左右居中*/
? ? ? ? ? text-align: center;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header .icons{
? ? ? ? ? padding: 0 16px;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header .icons:hover{
? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? height: 42px;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header .user {
? ? ? ? ? width: 160px;
? ? ? ? ? height: 42px;
? ? ? ? ? /*默认头像附近颜色*/
? ? ? ? ? font-family: var(--monospace); position: relative; display: inline-block;"> CornflowerBlue;
? ? ? ? ? /*下拉框字体颜色*/
? ? ? ? ? color: #fafbfd;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header .user:hover {
? ? ? ? ? font-family: var(--monospace); position: relative; display: inline-block;"> rgba(49,64,94,.5);
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header .user .a img {
? ? ? ? ? height: 38px;width: 38px; margin-top: 3px; border-radius: 50%;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header .user .b {
? ? ? ? ? z-index: 20;
? ? ? ? ? position: absolute;
? ? ? ? ? top: 42px;
? ? ? ? ? right: 88px;
? ? ? ? ? width: 100px;
? ? ? ? ? /*下拉框背景颜色*/
? ? ? ? ? font-family: var(--monospace); position: relative; display: inline-block;"> CornflowerBlue;
? ? ? ? ? display: none;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header .user:hover .b{
? ? ? ? ? display: block;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-header .user .b a{
? ? ? ? ? display: block;
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-content .menu{
? ? ? ? ? position: absolute;
? ? ? ? ? top: 42px;
? ? ? ? ? left: 0;
? ? ? ? ? bottom: 0;
? ? ? ? ? width: 200px;
? ? ? ? ? /**/
? ? ? ? ? font-family: var(--monospace); position: relative; display: inline-block;"> #FFFFFF;
? ? ? ? ? min-width: 200px;
? ? ? ? ? overflow: auto;
? /*底部出现滚动栏*/
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? .pg-content .content{
? ? ? ? ? position: absolute;
? ? ? ? ? top: 42px;
? ? ? ? ? right: 0;
? ? ? ? ? bottom: 0;
? ? ? ? ? left: 200px;
? ? ? ? ? overflow: auto;
? ? ? ? ? z-index: 9;
? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? /*此处加上overflow和不加是两种布局风格,一种是跟菜单栏滑动,一种不跟*/
? ? ? }
?
? </style>
</head>
<body>
? <div class="pg-header">
? ? ? <div class="logo left">
? ? ? ? ? **配置平台
? ? ? </div>
?
?
? ? ? <div class="user right" style="position: relative;">
? ? ? ? ? <a class="a" href="#">
? ? ? ? ? ? ? <img src="1.png">
? ? ? ? ? </a>
? ? ? ? ? <div class="b">
? ? ? ? ? ? ? <a>个人中心</a>
? ? ? ? ? ? ? <a>注销</a>
? ? ? ? ? </div>
? ? ? </div>
?
? ? ? <div class="icons right" >
? ? ? ? ? <i class="far fa-comment-dots" ></i>
? ? ? ? ? <span style="font-size: 7px">3</span>
? ? ? </div>
? ? ? <div class="icons right">
? ? ? ? ? <i class="fab fa-facebook"></i>
? ? ? ? ? <span></span>
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
?
? <div class="pg-content">
? ? ? <div class="menu left">YouMen</div>
? ? ? <div class="content left">
? ? ? ? ? <div style="position: fixed; bottom: 0;right: 0;width: 30px;height: 30px;">/&;/div>
? ? ? ? ? ? <p>YouMendsafddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddd</p>
?
? ? ? </div>
? </div>
?
? <div class="pg-footer"></div>
</body>
</html>
?
?
?
?
?
? (编辑:李大同)
【声明】本站内容均来自网络,其相关言论仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本站立场。若无意侵犯到您的权利,请及时与联系站长删除相关内容!
|






